requests와 bs4를 사용해 웹크롤러 만들기
웹 크롤링 이란?
웹 크롤링(Crawling), 웹 스크래핑(Scraping)은 웹 상에서 원하는 정보(contents)를 수집, 분류, 저장하는 것을 의미한다. 데이터 과학, 빅데이터 그리고 머신러닝의 기본인 데이터 수집에 효과적으로 활용할 수 있다.
웹 크롤러 만들기
간단한 예제로 멜론 주간 차트를 크롤링 해보자.
웹 크롤러를 만들기 위해 HTML 및 XML 구문을 분석하기 위한 파이선 패키지인 Beautiful Soup과 http request를 위한 파이선 패키지 requests를 사용할 예정이므로, 파이썬 패키지 관리 시스템인 pip를 이용해 설치해 준다.
pip install bs4 requests
requests로 페이지 정보 가져오기
기본적으로 requests를 이용한 get 요청은 아래와 같이 사용할 수 있다.
# HTTP GET Request
req = requests.get('https://www.melon.com/chart/week/index.htm')
# HTML 소스 가져오기
html = req.text
단, 멜론 사이트는 추가적으로 header에 User-Agent가 필요하므로, 크롬 개발자 도구의 Network탭에서 User-Agent를 찾아 추가해 준다.
headers = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.150 Safari/537.36'}
url = 'https://www.melon.com/chart/week/index.htm'
req = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
html = req.text
print(html)
위의 코드를 실행하면 html 코드가 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
bs4로 파싱하여 원하는 데이터 수집하기
이렇게 수집되어진 html 문자열을, BeautifulSoup을 이용해 파싱해 준다.
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
이제, 원하는 태그, 클래스, 아이디 등을 이용해 데이터를 수집할 수 있다. 이를 위해서는 웹 페이지 내에서 내가 수집하고 싶은 콘텐츠가 어떤 구조의 html 코드로 이루어져 있는지 확인이 필요하다. 구글 크롬 개발자 도구에서 이를 확인할 수 있다.
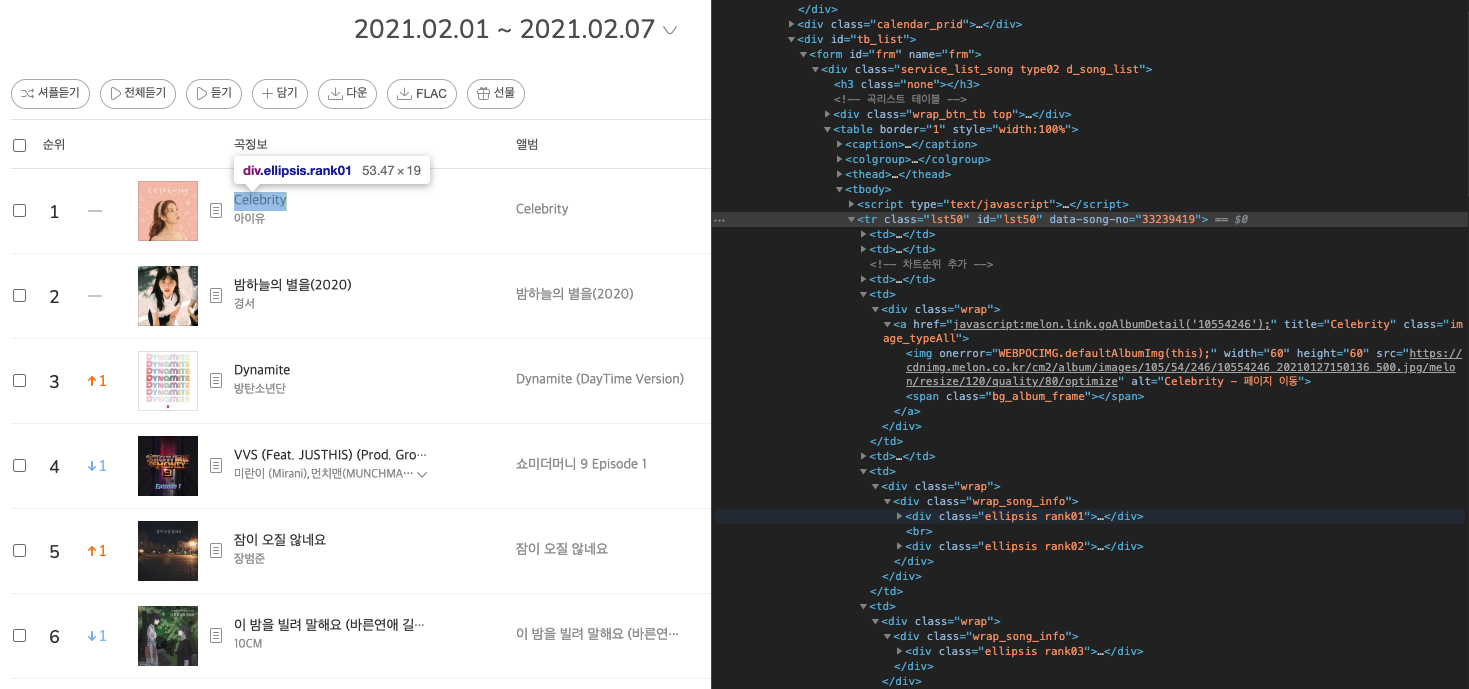
BeautifulSoup에서 크롤링에 사용되는 대표적인 메소드는 find_all()/select()와 find()/select_one()이다. find_all()/select()를 사용하면 해당 조건을 만족하는 전체 데이터를 얻을 수 있으며, find()/select_one()를 사용하면 조건을 만족하는 젤 첫 번째 데이터를 얻을 수 있다.
아래 코드로 멜론 주간 차트에 랭킹되어있는 곡의 앨범 커버 이미지 url, 곡명, 아티스트 명, 앨범 이름을 수집할 수 있다.
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
headers = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.150 Safari/537.36'}
url = 'https://www.melon.com/chart/week/index.htm'
req = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
html = req.text
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
albumImages = soup.find_all("a", {"class": "image_typeAll"})
titles = soup.find_all("div", {"class": "ellipsis rank01"})
artists = soup.find_all("div", {"class": "ellipsis rank02"})
albums = soup.find_all("div",{"class": "ellipsis rank03"})
melon_chart_week = []
for item in zip(albumImages, titles, artists, albums):
melon_chart_week.append(
{
'albumImageSrc': item[0].find('img')["src"],
'title': item[1].find('a').text,
'artist': item[2].find('a').text,
'album': item[3].find('a').text,
}
)
추출 데이터 csv 파일로 저장하기
추가적으로 추출한 데이터를 csv 파일로 저장해 보자. 이때 사용할 수 있는 라이브러리는 Pandas로, 행과 열로 이루어진 데이터 객체를 만들어 데이터를 다룰 수 있는 파이썬 데이터 분석 라이브러리이다.
먼저, pip를 이용해 pandas를 설치해 준다.
pip install pandas
설치가 되었으면, 파일의 상단에 pandas를 import 하고, 행과 열의 구조의 데이터 오브젝트인 DataFrame을 이용해 추출된 데이터를 csv 파일로 저장한다.
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import pandas as pd
headers = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.150 Safari/537.36'}
url = 'https://www.melon.com/chart/week/index.htm'
req = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
html = req.text
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser')
albumImages = soup.find_all("a", {"class": "image_typeAll"})
titles = soup.find_all("div", {"class": "ellipsis rank01"})
artists = soup.find_all("div", {"class": "ellipsis rank02"})
albums = soup.find_all("div",{"class": "ellipsis rank03"})
melon_chart_week = []
for item in zip(albumImages, titles, artists, albums):
melon_chart_week.append(
{
'albumImageSrc': item[0].find('img')["src"],
'title': item[1].find('a').text,
'artist': item[2].find('a').text,
'album': item[3].find('a').text,
}
)
data = pd.DataFrame(melon_chart_week)
data.to_csv('melon_chart_week.csv')
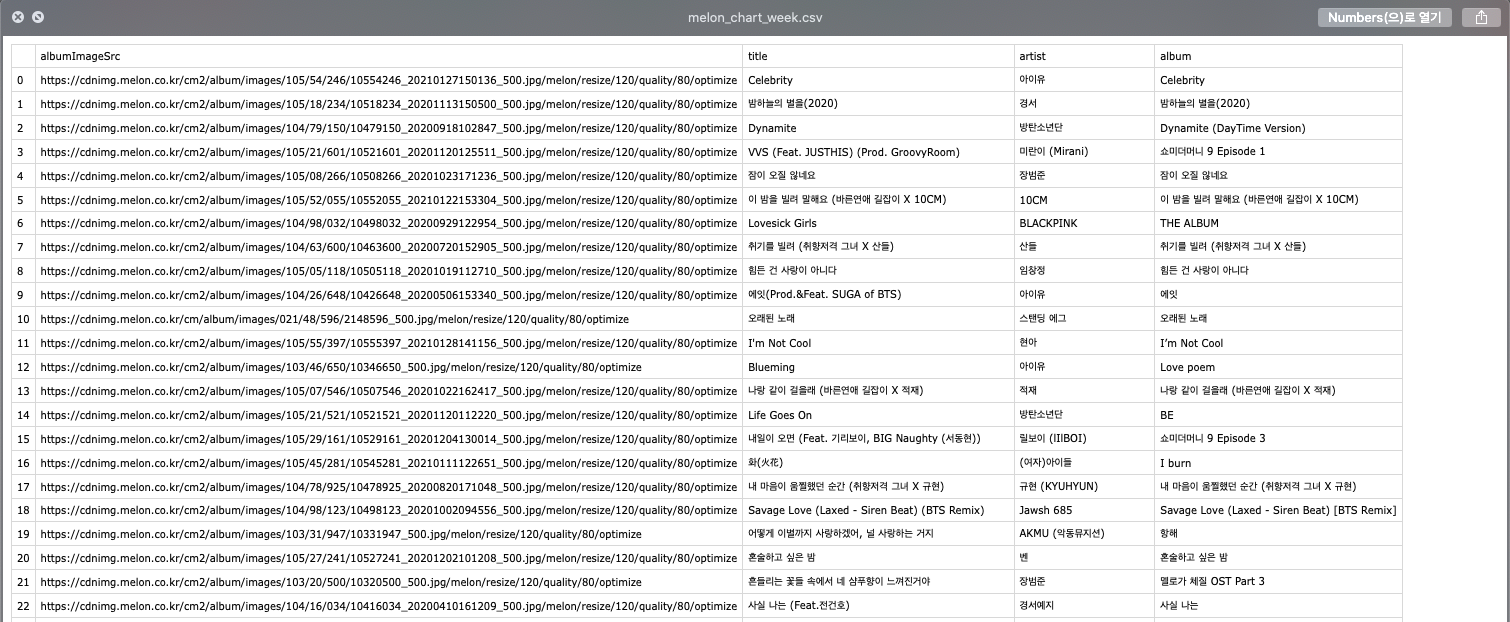
최종적으로 실행하면 아래와 같은 csv 파일이 만들어지는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
👩🏻💻 배우는 것을 즐기는 프론트엔드 개발자 입니다
부족한 블로그에 방문해 주셔서 감사합니다 🙇🏻♀️
in the process of becoming the best version of myself